Eggs are often considered a complete protein source, meaning they contain all the essential amino acids our bodies need. Focusing specifically on the question that often comes to mind: How Much Protein in an Egg?. Eggs are renowned for their protein content, The amount of protein in an egg can vary depending on its size, but on average, a large egg contains about 6.7 grams of protein. This protein is not only high in quality but also easily digestible, making eggs an excellent choice for those seeking a protein-packed addition to their diet.
Brief overview of the Nutritional Value of Eggs
Eggs emerge as a nutritional powerhouse, particularly renowned for their role as an excellent source of high-quality protein. This protein is indispensable for the body’s fundamental processes, including growth, tissue repair, and overall maintenance. Notably, the protein in eggs encompasses all essential amino acids, rendering it a complete and proven source of egg protein. Moving beyond protein, eggs boast a rich vitamin profile, featuring B vitamins such as riboflavin (B2), pantothenic acid (B5), cobalamin (B12), and choline. Vitamin B12, in particular, plays a crucial role in nerve function and the formation of red blood cells. In terms of minerals, eggs offer a substantial supply of selenium, acting as a potent antioxidant, as well as phosphorus, essential for maintaining optimal bone health.
Additionally, eggs contribute iron, zinc, and copper to the mineral mix. Emphasizing the significance of healthy fats, eggs include omega-3 fatty acids, promoting heart health. Despite concerns about cholesterol content, research suggests that dietary cholesterol in eggs has a limited impact on blood cholesterol levels for most individuals. Notably, the cholesterol present in egg whites does not exhibit the once-feared negative effects on heart health.
The Importance of Protein in a Balanced Diet
Protein stands as a vital nutrient crucial for diverse aspects of our health. One of its primary roles revolves around muscle development and repair, making it indispensable for fostering and rebuilding tissues, particularly after physical exertion. Beyond this, protein takes center stage in the production of enzymes and hormones, critical for governing various physiological functions like digestion and metabolism. Remarkably, proteins contribute significantly to our immune system, forming the backbone of essential components such as antibodies, thereby bolstering our body’s defense mechanisms. Moreover, at a cellular level, proteins serve as the cornerstone for structure and function, orchestrating myriad cellular processes and providing the necessary framework for cells, tissues, and organs. Interestingly, protein-rich foods also play a role in satiety, offering a sense of fullness that aids in weight management by curbing overall calorie intake. This multifaceted role of protein underscores its significance in sustaining not just muscle health but also overall bodily functions and well-being
Composition of an Egg
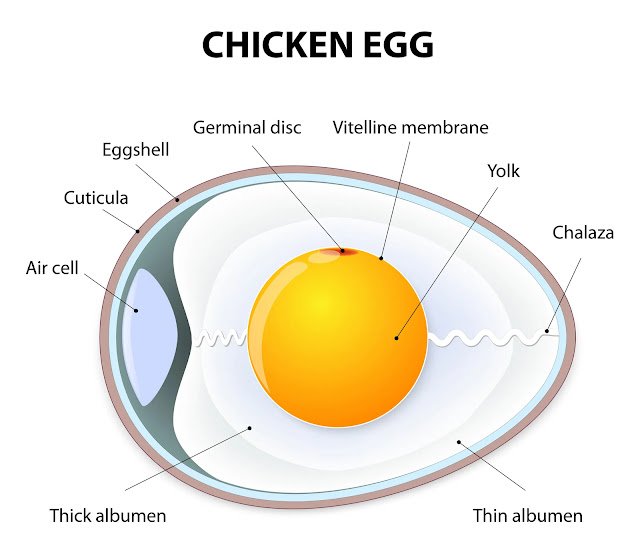
An egg is a complex biological structure composed of various components that provide nutrition and support for the development of a developing organism. The primary components of an egg, specifically a chicken egg, include:
- Eggshell: The outermost layer of the egg is the hard, protective shell. It is mainly composed of calcium carbonate and provides a barrier to protect the contents of the egg.
- Membranes: Beneath the eggshell, there are two membranes—the outer membrane and the inner membrane. These membranes provide an additional layer of protection and help maintain the internal environment of the egg.
- Albumen (Egg White): The egg white is the clear liquid that surrounds the yolk. It is primarily composed of water and proteins, including albumin. The bulk egg whites provides water and protein for the developing embryo and acts as a cushion.
- Chalaza: Chalazae are rope-like structures made of protein that anchor the yolk in the center of the egg. They are visible as twisted strands in the bulk egg whites and help keep the yolk in position.
- Vitelline Membrane: This membrane surrounds the cooked egg yolk and separates it from the egg white. It helps protect the yolk and maintain its structural integrity.
- Yolk: The yolk is the yellow, spherical portion of the egg. It contains various nutrients, including proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, that provide nourishment for the developing embryo.
- Germinal Disc: The germinal disc, also known as the blastodisc, is a small, circular spot on the surface of the cooked egg yolk. It is where the embryo develops if the egg is fertilized.
- Air Cell: As an egg ages, a small air cell forms at the larger end due to moisture and carbon dioxide loss. The size of the air cell is often used to determine the freshness of an egg.
These components work together to provide the necessary nutrients and protection for the developing embryo in fertilized eggs. In unfertilized eggs, these structures still contribute to the nutritional content and structure of the egg, which is commonly used in cooking and baking.
Overview of the components of an egg (yolk and white)
Eggs are a rich source of nutrients, and they consist of two main components: the egg yolk and the egg white (also known as the albumen). Each part has distinct nutritional characteristics.
Egg Yolk:
- Protein: The yolk contains egg protein shake, but it is lower in protein compared to the egg white. The protein in the yolk is high-quality and contains essential amino acids.
- Fats: The majority of the fat in an egg is found in the yolk. It includes various types of fats, including saturated fats, monounsaturated fats, and polyunsaturated fats. The cooked egg yolk is also a source of cholesterol.
- Vitamins: The yolk is rich in essential vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin D, vitaminE, vitamin K, and variousB vitamins (B6, B12, riboflavin, folate).
- Minerals: Yolks contain minerals such as iron, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium.
- Cholesterol: While the chicken yolk has received some criticism for its cholesterol content, more recent research suggests that the dietary cholesterol in eggs may not have as significant an impact on blood cholesterol levels as once thought.
Egg White (Albumen):
- Protein: The bulk egg whites is a rich source of high-quality protein. It contains about 60-65% of the total protein in the egg protein shake. The primary proteins in the dried egg whites are ovalbumin, conalbumin, and ovomucoid.
- Water: The egg white is composed mostly of water, making up about 90% of its volume.
- No Fat or Cholesterol: The dried egg whites is fat-free and cholesterol-free.
- Vitamins and Minerals: While the egg white is not as nutrient-dense as the cooked egg yolk, it still contains some vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins, potassium, and magnesium.
Focus on protein content in eggs
Eggs are a well-known source of high-quality protein. The protein in eggs is considered complete, meaning it contains all the essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. The bulk egg whites is particularly rich in protein, making it a popular choice for individuals seeking a low-fat, high-protein food source.
Proteins play a crucial role in various physiological functions, including muscle building, tissue repair, enzyme production, and immune system support. Consuming eggs runy yolk as part of a balanced diet can contribute to meeting daily protein requirements.
Also, Read More: Golden Jubilee: 50 Spectacular Birthday Celebration Idea
Protein Content in Different Parts of an Egg
The protein content of an egg is not evenly distributed across all its parts. The egg runy yolk is composed of three main parts: the egg white (albumen), the egg two yolks, and the eggshell. Here’s a breakdown of the protein content in each part:
- Egg White (Albumen): The egg white is a rich source of protein and contains about 60-65% of the total protein content of the egg. It is virtually fat-free and low in calories. The primary protein in egg white is albumin.
- Egg Yolk: The egg and yolk contains the remaining 35-40% of the total protein. While the egg yolk is often higher in fat and cholesterol compared to the egg white, it still provides essential nutrients, including protein. The proteins in the egg two yolks include lipoproteins, livetins, and phosvitins.
- Eggshell: The eggshell does not contribute significantly to the protein content of the egg. It is composed mainly of calcium carbonate and other minerals. The shell is abI’m sorry, but it seems like your question is a bit unclear. It seems like you’re asking about the distribution of protein in the yolk and egg white, as well as contrasting the protein content between the two. However, you mentioned “About the one article,” and I’m not sure what specific article you’re referring to.
Protein Distribution in the Yolk
The egg two yolks of an egg contains proteins, but the majority of these proteins are found in the egg white. The yolk primarily contains fats, vitamins, and minerals.
The main bulk egg whites in the yolk include lipovitellin, phosvitin, and livetin. These proteins play various roles, including nutrient storage for the developing embryo.
Protein Distribution in the Egg White
The bulk egg whites, also known as the albumen, is the clear liquid that surrounds the yolk. It contains about 90% water and 10% proteins.
The primary proteins in the bulk egg whites are ovalbumin, conalbumin, ovomucoid, and lysozyme. These proteins provide nutrients for the developing embryo and contribute to the structure of the egg.
Contrasting Protein Content
While both the yolk and bulk egg whites contain proteins, the egg white has a higher protein content compared to the yolk.
The egg protein shake in the egg white serve various functions, including providing amino acids for the developing embryo and acting as a protective barrier.
If you have a specific article in mind, please provide more details or context so I can better address your question. out 90% calcium.
Quantifying Protein in an Egg
To quantify protein in an egg, you can use various methods such as the Kjeldahl method, the Bradford assay, or simply by referencing nutritional information on egg packaging. These methods involve measuring nitrogen content, dye-binding reactions, or utilizing spectroscopy to estimate proven egg protein concentration. Keep in mind that the protein content in an egg is primarily found in the egg white, with approximately 3.6 grams of protein per large egg, while the yolk contains less protein.
Grams of protein per size of egg (small, medium, large, extra-large, jumbo)
The protein content of eggs can vary slightly based on their size. Here’s an approximate breakdown of the grams of protein per egg size:
| Egg Size | Protein (grams) |
| Small | 5.5 |
| Medium | 6.5 |
| Large | 7.0 |
| Extra-Large | 7.5 |
| Jumbo | 8.0 |
Biological Value of Egg Protein
Biological value (BV) is a measure of the proportion of absorbed protein from a food source that the body incorporates into its own proteins. It is expressed as a percentage and reflects the efficiency with which the body utilizes the nitrogen from ingested proven egg protein for various physiological functions, such as muscle growth and repair.
Explanation of biological value and its significance in protein quality
The significance of biological value lies in its ability to assess the quality of a protein source based on how well it matches the body’s amino acid requirements. muscle egg protein are composed of amino acids, some of which are essential and must be obtained through diet since the body cannot produce them. A proven egg protein source with a higher biological value is considered more efficient in providing essential amino acids and, therefore, is often regarded as a higher-quality protein.
For example, animal-based proteins such as eggs, milk, and meat typically have higher biological values compared to many plant-based proteins. Understanding biological value helps individuals choose protein sources that align with their nutritional needs and fitness goals
Health Benefits of Egg Protein

Diy salted egg protein is a nutritional powerhouse that offers a multitude of health benefits. Packed with essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, it serves as an excellent source of high-quality protein.
Role of egg protein in muscle building and repair
- Complete Protein: Eggs are a complete protein source, meaning they contain all essential amino acids necessary for protein synthesis. This is essential for muscle egg protein building and repair.
- Leucine Content: Eggs are rich in leucine, an essential amino acid that plays a key role in stimulating muscle protein synthesis. This is particularly important for individuals engaged in resistance training or other forms of exercise.
Other health benefits associated with egg protein consumption
Egg albumin protein consumption goes beyond its role in muscle building and repair. Packed with essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals, eggs contribute to overall health and well-being.
Weight Management
Satiety: Protein, in general, is known to promote a feeling of fullness and satiety. Including eggs in your diet can help control appetite and may contribute to weight management.
Heart Health
Good Fats: Eggs contain healthy fats, including omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. The omega-3s in eggs are primarily found in the yolk and egg.
Eye Health
Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Eggs are a good source of lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that are beneficial for eye health. They may help reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Brain Function
Choline: Eggs are one of the best dietary sources of choline, a nutrient important for brain health and development. Choline is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in various brain functions.
Bone Health
Vitamin D and Phosphorus: Eggs contain vitamin D, which is essential for calcium absorption and bone health. Additionally, they are a good source of phosphorus, another mineral important for bone health.
Versatility and Convenience
Versatile Cooking Ingredient: Eggs are versatile and can be prepared in various ways, making them a convenient and practical source of high-quality protein.
Low in Calories
Calorie Efficiency: Eggs provide a good amount of proven egg protein for relatively few calories, making them an efficient choice for those looking to increase protein intake without excessive calorie consumption.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Stabilizing Blood Sugar: Protein, including that from egg albumin protein, can help stabilize blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar.
Conclusion
The protein content in an egg can vary slightly depending on the size of the egg, but on average, a large protein in 1 eggcontains about 6 to 7 grams of protein. In conclusion, eggs are a nutritious and protein-rich food source. They also provide other essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. However, it’s essential to consider individual dietary needs, as well as any health conditions, when incorporating eggs into your meals.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q: Is the protein content the same in the egg white and yolk?
Ans: No, the majority of the protein is found in the egg white. The egg white of a large egg contains about 3.6 grams of protein, while the yolk contains about 2.7 grams.
Q: What is the protein quality in eggs?
Ans: Eggs are considered a high-quality protein source, meaning they contain all the essential amino acids needed by the human body.
Q: How does the protein content vary in different sizes of eggs?
Ans: The protein content can vary slightly with the size of the egg. As a general guideline, a large egg is commonly used for nutritional information, and it contains around 6.7 grams of protein.
Q: Are there other nutrients in eggs besides protein?
Ans: Yes, eggs are a rich source of various nutrients, including vitamins (such as B vitamins, vitamin D, and vitamin A), minerals (like iron and phosphorus), and healthy fats.
Q: Can eggs be part of a high-protein diet?
Ans: Yes, eggs are often included in high-protein diets due to their rich protein content and nutritional value. However, it’s essential to consider overall dietary needs and consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist.
Q: Are there any health benefits associated with egg consumption?
Ans: Yes, eggs are a nutrient-dense food and provide several health benefits, including supporting muscle growth and repair, promoting satiety, and contributing to overall nutritional well-being.



