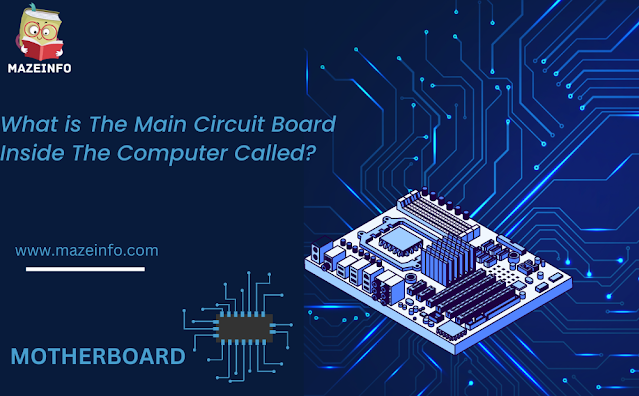
In the vast realm of modern computing, the beating heart of every electronic marvel lies within a crucial component known as the motherboard. At the core of this intricate digital ecosystem, the question arises: “What is the main circuit board inside the computer called?” This fundamental inquiry unveils the motherboard’s pivotal role in connecting and orchestrating the various components that together empower the computers to perform its myriad functions. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the significance and intricacies of this central hub that serves as the backbone of our digital devices.
Power Delivery Overview
Power delivery is a critical aspect of electronic systems, ensuring that devices receive the necessary electrical power supply to function optimally. This process involves the transmission of electrical energy from a power source to the components that require it. In the context of computers and other electronic devices, power delivery is facilitated through standardized connectors and interfaces. Two prominent connectors in this realm are the ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) and EPS (EPS12V) connectors, each playing a key role in delivering power to different components within a computer system.
ATX Connector
The ATX connector is a standard power supply connector widely used in desktop computers. It is designed to provide power to the motherboard and peripherals. The ATX power supply typically features a 20-pin or 24-pin main board circuit power connector, delivering power to the motherboard. Additionally, it includes various auxiliary connectors for components such as hard drives, optical drives, and expansion cards. The ATX specification has evolved over time to meet the increasing power demands of modern computing systems.
EPS Connector
The EPS (Extended Power Supply) connector, specifically EPS12V, is geared towards high-performance systems and servers. It is an extension of the ATX standard, addressing the need for additional power delivery to the CPU sockets and other power-hungry components. The EPS connector typically features an 8-pin or 4+4-pin design, providing dedicated power to the CPU. This ensures stable and efficient power delivery to meet the demands of demanding computing tasks, such as video rendering, gaming, or server operations.
Components on the Motherboard
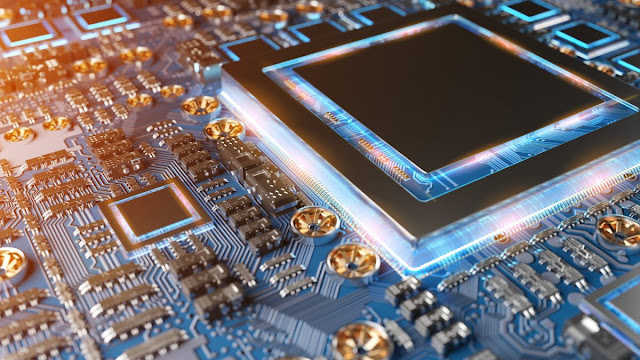
The motherboard is the central printed circuit board (PCB) in a computer that houses essential components and provides connectivity for various hardware components. Here are five important components on the motherboard, each playing a crucial role in the functioning of a computer:
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- The CPU is often considered the brain of the computer. It performs calculations and executes instructions, handling the majority of data processing tasks.
- The CPU socket on the motherboard is where the processor is installed. It connects to the motherboard via a socket and communicates with other components through the system bus.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
- RAM is volatile memory that provides temporary storage for data and program code that the CPU is actively using.
- RAM slots on the motherboard hold the RAM modules, and the memory controller facilitates communication between the RAM and the CPU.
Expansion Slots
- Expansion slots allow users to add additional hardware components to the motherboard, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and networking cards.
- Common types of expansion slots include PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots, which are versatile and widely used for various expansion cards.
Chipset
- The chipset is a set of integrated circuits on the motherboard that manages communication between the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and other peripherals.
- It includes the Northbridge and Southbridge chips, each with specific responsibilities. The Northbridge typically handles high-speed communication (e.g., between the CPU and RAM), while the Southbridge manages lower-speed tasks and connectivity (e.g., USB, SATA).
BIOS/UEFI Firmware
- The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) firmware is a piece of software stored on a ROM (Read-Only Memory) chip on the motherboard.
- It provides the basic instructions for the computer to boot up, initializes hardware components during the boot process, and acts as an interface between the operating system and the computer’s hardware.
Expansion Slots

Expansion slots are connectors on a computer’s motherboard that allow additional hardware components to be added to the system. These slots provide a way to expand and customize the capabilities of a computer by adding various peripherals and expansion cards. Expansion slots are standard in desktop computers and some larger laptops. Here are some common types of expansion slots:
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect): PCI slots were once a standard for connecting various expansion cards such as sound cards, network cards, and graphics cards. However, they have largely been replaced by PCIe in modern systems.
PCI Express (PCIe): PCIe is the most common expansion slot standard used in modern computers. It offers higher data transfer rates than PCI and supports various configurations, such as x1, x4, x8, and x16, indicating the number of data lanes. PCIe is commonly used for graphics cards, storage controllers, network cards, and other high-performance peripherals.
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): AGP was a dedicated expansion slot specifically designed for graphics cards. It has been largely phased out in favor of PCIe for modern systems.
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture): ISA slots were used in older computers for connecting peripherals like sound cards and network cards. However, ISA slots have become obsolete, and modern systems no longer support them.
AMR (Audio Modem Riser): AMR was a slot used for audio and modem cards. It was a short-lived standard and is no longer used in modern table computers.
PCI-X (PCI eXtended): PCI-X is an extended version of the PCI standard designed for high-performance applications and servers. It offers higher bandwidth than traditional PCI but has been largely replaced by PCIe in consumer systems.
DIMM Slots: While not typically considered traditional expansion slots, DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) slots on the motherboard serve as slots for system memory (RAM) modules, allowing users to expand the desktop computer memory capacity.
Input Output Ports

Input output (I/O) ports are interfaces on electronic devices that allow them to communicate with other devices or systems. These ports facilitate the transfer of data, power, or signals between the device and external components. Different devices have various types of ports, each serving a specific purpose. Here are some common types of input/output ports:
USB (Universal Serial Bus) Ports
- USB ports are versatile and widely used for connecting peripherals such as keyboards, mice, printers, external storage devices, and more.
- USB comes in various versions, such as USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, and USB-C, each with different data transfer speeds and capabilities.
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) Ports
- HDMI ports are commonly found on devices like TVs, monitors, and audio-visual equipment.
- They transmit high-definition video and audio signals through a single cable.
Ethernet Port
- This port is used for wired network connections, allowing devices to connect to a local area network (LAN) or the internet.
Audio Ports
- These ports are used for connecting headphones, microphones, speakers, and other audio devices.
- Common audio jacks include 3.5mm and 1/4-inch connectors.
VGA (Video Graphics Array) Port
- VGA ports are older and less common now but are still found on some monitors and projectors.
- They transmit analog video signals.
DisplayPort
- Similar to HDMI, DisplayPort is used for transmitting video and audio signals.
- It is commonly found on server computers and monitors.
Thunderbolt
- Thunderbolt ports support high-speed data transfer, video output, and power delivery.
- They are often found on newer laptops and external storage devices.
SD Card Slot
- SD card slots are used for reading and writing data to SD cards commonly used in cameras and other portable devices.
Power Port
- This is where the device receives power, either through a power adapter or a USB connection.
Serial and Parallel Ports (Less Common)
- Serial ports (e.g., RS-232) and parallel ports were more common in older devices for connecting peripherals like printers and modems. However, they are largely obsolete now.
Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
The Basic Input Output System, commonly known as BIOS, is a fundamental component of computer systems that plays a crucial role in the initialization and management of hardware. BIOS serves as the interface between the operating system and the computer’s hardware components, facilitating essential functions such as the booting microprocess, hardware configuration, and communication between the operating system and peripherals.
Overview of BIOS
BIOS, typically stored in a read-only memory (ROM) chip on the computer’s motherboard, provides a set of low-level routines that enable the operating system to communicate with hardware components. During the boot process, BIOS initializes the system, conducts a Power-On Self-Test (POST) to check hardware integrity, and then locates and loads the operating system into the computer’s memory. It acts as a bridge between the hardware and software layers, ensuring a seamless interaction between the two.
BIOS Configuration
Users can access and configure various settings in the BIOS, such as system date and time, boot device priority, and hardware parameters. This configuration interface allows users to customize the behavior of their system, ensuring compatibility with specific hardware components and optimizing overall performance.
Also, Read More: Top Creative Among Us Party Ideas for Unforgettable Fun!
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
.jpg)
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, or UEFI, represents a modern replacement for traditional BIOS firmware. UEFI is designed to provide a more advanced and versatile interface for managing the system firmware and boot process. Unlike BIOS, UEFI is not limited to a specific architecture, allowing for greater flexibility and enhanced functionality.
Key Features of UEFI
UEFI introduces several advancements over BIOS, including support for larger storage capacities, faster boot times, and a graphical user interface for easier navigation and configuration. It also supports 64-bit architectures, enabling systems to take full advantage of modern hardware capabilities.
Secure Boot and Compatibility
One notable feature of UEFI is Secure Boot, a security mechanism that helps protect against unauthorized firmware and operating system loaders during the boot process. UEFI’s compatibility with the GUID Partition Table (GPT) also allows for efficient management of large disk capacities, surpassing the limitations of the older Master Boot Record (MBR) used by BIOS.
Transition from BIOS to UEFI
While UEFI offers numerous benefits, the transition from BIOS to UEFI may require careful consideration and proper implementation. Many modern computers come with UEFI by default, but older systems may need a firmware update or a motherboard replacement to adopt UEFI fully.
Form Factor
It seems like your question got cut off, but I believe you’re asking about different motherboard form factors. Here are some common form factors:
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended): This is the most common form factor for desktop motherboards. ATX motherboards are larger and offer more expansion slots compared to smaller form factors.
MicroATX (mATX): MicroATX is a smaller form factor compared to ATX. It usually has fewer expansion slots and a smaller overall footprint. MicroATX motherboards are a good choice for smaller cases and budget systems.
Mini-ITX: Mini-ITX is even smaller than MicroATX and is designed for compact and space-constrained builds. While it has fewer expansion slots, it’s a popular choice for small form factor (SFF) and mini PCs.
Extended ATX (EATX): EATX motherboards are larger than standard ATX motherboards. They offer more expansion slots and are often used in high-end gaming and workstation systems where additional features and performance are required.
ITX Form Factors (e.g., Nano-ITX, Pico-ITX): These are even smaller form factors designed for specific applications. Nano-ITX and Pico-ITX, for example, are extremely compact and are used in applications where space is a critical factor, such as embedded systems.
Conclusion
The main circuit board inside a computer is commonly referred to as the motherboard. The motherboard serves as the central hub for connecting various hardware components, including the processor (CPU), main memory (RAM), storage devices, graphics card, and other peripherals. It facilitates communication and data transfer among these components, allowing the computer to function as a cohesive system. The motherboard plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and performance of a computer, serving as the foundation for the integration and coordination of its internal components.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the function of the motherboard?
Ans: The motherboard serves as the central hub for connecting various components of a computer, such as the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and expansion cards. It facilitates communication between these components.
Q: Why is it called a “motherboard”?
Ans: The term “motherboard” is derived from the fact that it is the main board that houses and connects all the essential components of a computer, similar to how a mother nurtures and connects a family.
Q: What are the key components on the motherboard?
Ans: Major components on a motherboard include the Central Processing Unit (CPU) socket, Random Access Memory (RAM) slots, expansion slots (PCIe, etc.), connectors for storage devices (SATA, M.2), and peripheral connectors (USB, audio, etc.).
Q: How does the motherboard impact computer performance?
Ans: The motherboard plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance and capabilities of a computer. The quality of components, support for various technologies, and overall design influence the system’s speed, stability, and expandability.
Q: How does the motherboard impact computer performance?
Ans: The motherboard plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance and capabilities of a computer. The quality of components, support for various technologies, and overall design influence the system’s speed, stability, and expandability.
Q: Can you upgrade the motherboard in a computer?
Ans: Yes, but upgrading the motherboard often involves replacing other components, such as the CPU and RAM, to ensure compatibility. It’s a significant undertaking and is typically done when upgrading to a new generation of technology or when seeking specific features not supported by the current motherboard.