In today’s digital age, where online interactions dominate our daily lives, the need for secure access to websites has become paramount. As cyber threats continue to evolve, businesses and individuals alike are seeking robust solutions to safeguard their data and privacy. One technology that stands out in this realm is Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption. “What technology provides secure access to websites” SSL technology provides secure access to websites by encrypting the data exchanged between a user’s web browser and the website’s server, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from unauthorized access. In this article, we will delve deeper into how SSL encryption works and why it is a crucial component of online security.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Technology

SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) technology is a standard security protocol that establishes encrypted links between a web server and a browser in online communication. It ensures that all data passed between the web server and browsers remain private and integral. Here are some key points about SSL technology:
Encryption: SSL uses encryption algorithms to scramble data during transmission, making it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information such as credit card numbers, login credentials, and personal details.
Authentication: SSL certificates are used to verify the identity of websites. When a browser connects to a server secured with SSL, it checks the SSL certificate to confirm the server’s identity. This helps users trust that they are interacting with the legitimate website security services and not a malicious entity impersonating it.
Data Integrity: SSL also ensures data integrity, meaning the information exchanged between the server and browser remains unchanged and uncorrupted during transmission. This prevents data tampering or modification by unauthorized parties.
HTTPS: SSL is commonly implemented through HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), which is the secure version of HTTP. Websites using HTTPS encrypt data using SSL, providing a site secure and trusted environment for online interactions.
SSL/TLS: While SSL was widely used in the past, it has been largely replaced by TLS (Transport Layer Security), which is an updated and more secure site protocol. However, the term “SSL” is still commonly used to refer to both SSL and TLS technologies.
Uses: SSL/TLS technology is essential for securing online transactions, such as e-commerce purchases, online banking, and sensitive data transfers. It is also used to secure email communications, file transfers, and other types of online interactions where website privacy and security are critical.
SSL Certificates: To enable SSL on a website, an SSL certificate is required. This certificate is issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) and contains information about the open website, its owner, and the cryptographic keys used for encryption. Websites need to renew their SSL certificates periodically to maintain security.
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
TLS, or Transport Layer Security, is a protocol that ensures privacy between communicating applications and their users on the internet. It’s essential for securing data transfers and online communications, especially sensitive ones like financial transactions or personal information exchanges.
TLS works by encrypting data to make it unreadable to anyone who might intercept it. It also provides authentication to confirm the identity of the communicating parties and ensures data integrity to prevent tampering.
Here are some key aspects of TLS:
Encryption: TLS uses encryption algorithms to scramble data, making it unreadable without the correct decryption key. This protects data from being intercepted and understood by unauthorized parties.
Authentication: TLS supports various authentication methods, such as digital certificates, to verify the identities of the communicating parties. This prevents man-in-the-middle attacks where an attacker poses as one of the parties.
Data Integrity: TLS uses hash functions to ensure that data remains unchanged during transmission. This prevents data from being altered or corrupted by unauthorized parties.
Protocol Versions: TLS has evolved over time, with different versions like TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, TLS 1.3, and newer drafts offering improvements in web security, performance, and cryptographic algorithms.
Handshake Protocol: When a TLS connection is established, a handshake protocol occurs where the server and client negotiate the encryption algorithms and exchange cryptographic keys.
Usage: TLS is widely used in securing web browsing (HTTPS), email communication (SMTP, IMAP, POP3), virtual private networks (VPNs), and many other applications that require secure data transmission over the internet.
HTTPS HTTPS Protocol
The HTTPS protocol, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is an extension of HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) used for secure communication over a computer network, commonly the internet. It adds a layer of encryption to ensure that data exchanged between a web hosting security browser and a website remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
HTTPS uses SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols to establish a secure connection. This encryption process encrypts the data transferred between the client (web browser) and the server, making it difficult for third parties to intercept or read the information.
HTTPS is widely used for sensitive transactions on the web, such as online banking, e-commerce transactions, and accessing personal accounts. It helps protect user privacy and security by preventing attackers from eavesdropping or tampering with the data being transmitted. Websites using HTTPS are indicated by a padlock icon in the browser security address bar, providing users with visual assurance of a secure connection.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
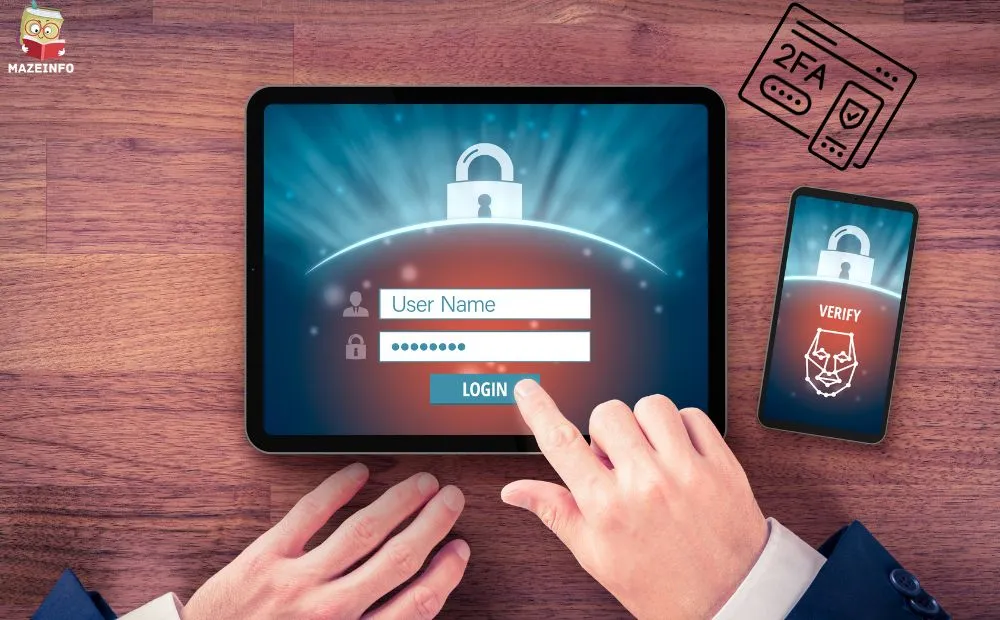

Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security measure designed to add an extra layer of website protection to online accounts. It requires users to provide two forms of identification before accessing their accounts, typically something they know (like a password) and something they have (like a mobile device).
The most common types of 2FA include:
- SMS-based 2FA: Users receive a one-time code via SMS on their registered mobile phone, which they enter along with their password to log in.
- Authentication apps: Users install an authentication app like Google Authenticator, Authy, or Microsoft Authenticator. These apps generate a time-sensitive code that users enter along with their password to log in.
- Hardware tokens: Physical devices like USB keys or smart cards generate codes that users enter during login. These are less common for consumer accounts but are used in some enterprise environments.
Secure Access Gateways
A secure access gateway, also known as a secure remote access gateway or simply a remote access gateway, is a type of network website security device or software that provides secure access to resources, applications, and data from remote locations or external networks. These gateways play a crucial role in ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information while maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the resources being accessed.
Here are some key aspects of secure access gateways:
Authentication: Secure access gateways typically use strong authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of users before granting them access. This may include multi-factor authentication (MFA), smart cards, biometric authentication, or other secure methods.
Encryption: They use encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS or IPsec to create secure tunnels for data transmission between the remote user and the internal network. This helps protect data from eavesdropping or interception by unauthorized parties.
Access Control: Gateways enforce access control policies based on user credentials, device posture, and other contextual information. They can restrict access to specific resources or segments of the network based on predefined rules.
Endpoint Security: Many secure access gateways include features for endpoint security, such as host checking, antivirus scans, and endpoint compliance checks. This helps ensure that only secure and compliant devices can connect to the network.
Single Sign-On (SSO): Some gateways support single sign-on functionality, allowing users to access multiple resources with a single set of credentials. This improves user experience and reduces the risk of password fatigue or reuse.
Auditing and Logging: Secure access gateways often include logging and auditing capabilities to track access attempts, monitor user activity, and generate reports for compliance purposes. This helps organizations maintain visibility into who is accessing their resources and what they are doing.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Understanding Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
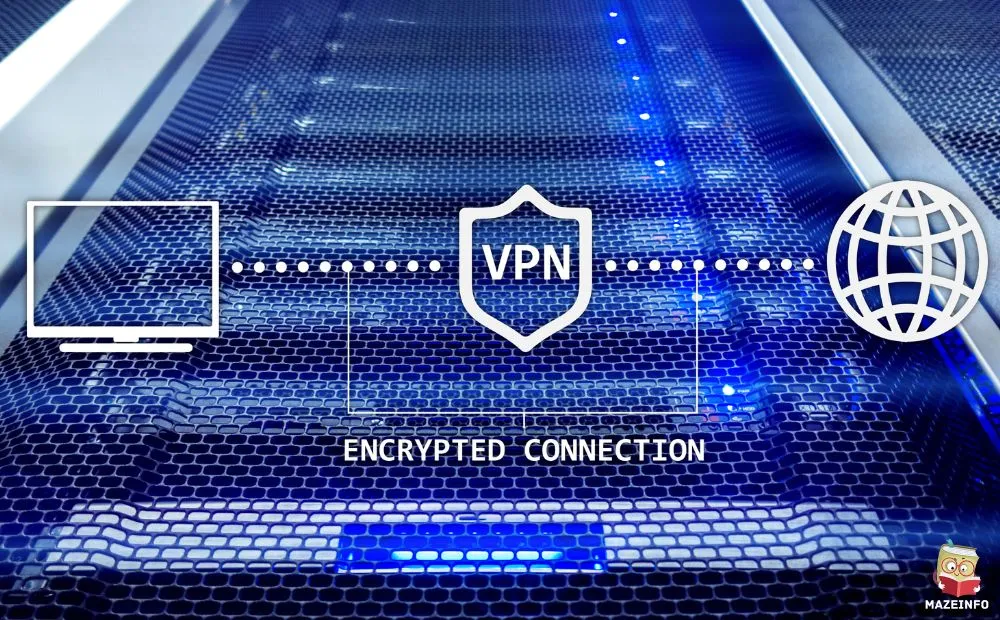
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) play a crucial role in ensuring online security, privacy, and unrestricted access to information. What is a VPN? Essentially, a VPN is a service that creates a secure and encrypted connection over the internet, allowing users to browse the web anonymously and securely. How Does a VPN Work? VPNs function by routing your isecure internet access traffic through a remote server operated by the VPN provider, masking your IP address and encrypting your data to prevent third parties from monitoring your online activities.
Benefits of Using a VPN include safeguarding sensitive information from hackers, bypassing geo-restrictions to access region-locked content, and maintaining anonymity while browsing. Types of VPNs range from remote access VPNs used by businesses to secure employee connections, to consumer VPNs for personal privacy and security. Overall, VPNs have become essential tools for ensuring online privacy and security in an increasingly interconnected digital world.
Also Read More: Exploring Advances in Electrical Technology for a Smarter Tomorrow
Secure Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) are crucial components in modern cybersecurity. They sit between a web application and the internet, monitoring and filtering HTTP traffic to protect against various attacks. A Secure Web Application Firewall (WAF) typically includes advanced features beyond basic firewall capabilities to offer comprehensive protection. Here are some key aspects of Secure WAFs:
Application Layer Protection: Secure WAFs focus on protecting the application layer of the OSI model, where web applications operate. They analyze HTTP requests and responses to detect and block malicious traffic targeting vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and command injection.
Signature-Based and Behavior-Based Detection: They employ both signature-based and behavior-based detection techniques. Signature-based detection involves comparing HTTP traffic against known attack patterns, while behavior-based detection looks for abnormal patterns that indicate potential attacks, such as unexpected traffic spikes or anomalous user behavior.
Custom Rule Creation: Secure WAFs allow administrators to create custom rules tailored to their specific applications and security requirements. These rules can define how the WAF should handle different types of traffic, such as blocking or allowing certain HTTP methods, URI patterns, or request headers.
Logging and Monitoring: They provide detailed logging and monitoring capabilities, allowing security teams to analyze traffic patterns, track security events, and investigate potential threats. This data is invaluable for incident response, compliance reporting, and ongoing security analysis.
Integration with Threat Intelligence: Many Secure WAF solutions integrate with threat intelligence feeds to enhance their detection capabilities. They can automatically update their rule sets based on the latest threat intelligence, ensuring protection against emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
SSL/TLS Inspection: Secure WAFs support SSL/TLS inspection to decrypt and inspect encrypted HTTPS traffic. This enables them to detect and block threats hidden within encrypted communication channels, such as malware payloads or malicious scripts.
Scalability and Performance: They are designed for scalability and high performance to handle large volumes of web traffic without impacting application performance. This includes features like load balancing, caching, and distributed architecture for efficient traffic processing.
API Protection: With the increasing use of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) in modern web applications, Secure WAFs often include features specifically designed to protect APIs. This includes validating API requests, enforcing rate limiting, and preventing API abuse.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)

Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two or more forms of identification before accessing an account or system. This additional layer of security enhances protection against unauthorized access and helps safeguard sensitive information. Here are some key points about Multi-Factor Authentication:
Enhanced Security: MFA provides an extra layer of security beyond just a username and password. By requiring additional factors such as a code sent to a mobile device or a biometric scan, MFA makes it harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
Protection Against Credential Theft: Traditional login credentials like passwords can be easily stolen or guessed. MFA mitigates this risk by adding a second or third factor that is more difficult for attackers to replicate.
Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory standards and industry guidelines require organizations to implement MFA as part of their security protocols. This includes standards like PCI DSS for payment processing and GDPR for data protection.
User Convenience: While MFA adds an extra step to the login process, modern implementations are designed to be user-friendly. Methods such as push notifications or biometric authentication can actually enhance the user experience while maintaining security.
Adaptive Authentication: Some MFA systems use adaptive authentication, which assesses risk factors such as the user’s location, device used, and recent activity to determine the level of authentication required. This dynamic approach strengthens security without inconveniencing legitimate users.
Phishing Resistance: MFA helps mitigate the effectiveness of phishing attacks. Even if a user unwittingly provides their login credentials through a phishing website safety, the attacker would still need the additional factor to gain access.
Scalability: MFA solutions are scalable and can be implemented across various platforms and devices, making them suitable for both small businesses and large enterprises.
Password Password Managers
Password managers are essential tools for anyone who values online security. They provide a secure way to store and organize passwords for various accounts, ensuring that each password is unique and complex. With a password manager, users only need to remember one master password to access all their other passwords. This significantly reduces the risk of password reuse or using weak passwords. Additionally, password managers often offer features like password generation, secure sharing, and encrypted storage, further enhancing security. Overall, using a password manager is a proactive step towards protecting sensitive information and maintaining digital privacy.
Biometric Authentication

Biometric authentication is revolutionizing the way we secure our digital and physical spaces. Unlike traditional methods such as passwords or PINs, which can be forgotten, stolen, or shared, biometric authentication uses unique physical characteristics like fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, or voiceprints to verify identity. This security technology offers a high level of security by making it nearly impossible for unauthorized individuals to gain access, as each person’s biometric data is distinct and cannot be easily replicated. With the growing concerns about data breaches and identity theft, biometric authentication provides a reliable and convenient solution for ensuring secure access to sensitive information, devices, and premises.
Conclusion
Secure access to websites is primarily provided by Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. These technologies establish encrypted connections between web browsers and servers, ensuring that sensitive information such as login credentials, financial transactions, and personal data remain protected from unauthorized access or interception by malicious actors. In conclusion, SSL/TLS technology plays a crucial role in safeguarding online communication and enabling secure access to websites, thereby fostering trust and confidence among users in the digital realm.
Q: What is SSL/TLS?
Ans: SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are protocols that encrypt data exchanged between a user’s browser and a website’s server, ensuring secure communication and protecting sensitive information like passwords and credit card details.
Q: How does HTTPS enhance website security?
Ans: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a combination of HTTP and SSL/TLS protocols. It encrypts data during transmission, preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding against man-in-the-middle attacks.
Q: What are SSL certificates, and why are they important?
Ans: SSL certificates are digital certificates that authenticate the identity of a website and encrypt data sent between the user and the site. They establish trust and credibility, crucial for secure online transactions and protecting user privacy.
Q: What is two-factor authentication (2FA) and how does it secure website access?
Ans: Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification before accessing a website, typically something they know (like a password) and something they have (like a verification code sent to their phone).
Q: How do VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) contribute to secure website access?
Ans: VPNs create a secure, encrypted connection between a user’s device and a private network, masking their IP address and encrypting data. This helps protect against cyber threats, especially when accessing websites over public Wi-Fi networks.
Q: What role do firewalls play in website security?
Ans: Firewalls act as barriers between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules. They help prevent unauthorized access, malware, and other cyber threats from reaching a website’s server.